Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-12-17 Origin: Site








When you look at industrial solar power systems, you notice many key parts. Solar panels are the most popular and make up over 41% of the money earned. Inverters and charge controllers work better now and cost less. Battery storage is getting more popular because more companies want to save energy. You need to check how much electricity solar panels make, how their power goes down over time, and how fast they lose strength. Most solar systems lose about 0.75% of their power every year. This means you have to plan well for using them for a long time and for the cost.
Learn about the types of solar panels. Monocrystalline panels work well. Polycrystalline panels cost less money. Pick the type that fits your energy use and budget.
Think about how well solar panels work. Keep panels clean and cool for more energy. Clean them often to keep them working well.
Pick grid-tied or off-grid systems. Grid-tied systems cost less and are easy to care for. Off-grid systems give you more freedom but need more planning.
Check how well solar panels work and how fast they lose power. Good panels lose less power as time goes on. This means you get more energy for many years.
Use performance numbers to help you choose. Numbers like capacity factor and performance ratio help you compare systems. This helps you pick the best one for your business.

Photovoltaic systems are used in many big solar projects. These systems have panels that change sunlight into electricity. There are different kinds of panels you can pick. Monocrystalline panels work well and are good in low sunlight. Polycrystalline panels cost less and are good for big areas. Thin-film panels are flexible and do well in hot places. Bifacial panels use both sides to make more power. The table below shows how these panels are different:
| Type of PV System | Efficiency Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline Modules | 15-20% | Solar roofing, large-scale installations |
| Polycrystalline Modules | Comparable to mono, lower cost | Utility-scale solar farms, large commercial rooftops |
| Thin-Film Modules | Up to 20.3% | Utility-scale, large commercial rooftops, hot climates |
| Bifacial Modules | 21.5% | Solar farms, commercial and industrial rooftops |
You should think about how well panels work before you choose. Humidity can make panels lose over 34% of their power. High heat makes voltage and efficiency go down. Dust can lower how well panels work by almost 29%. If panels are in the shade, they get less sunlight and make less energy. Wind can help cool panels and make them work better. To get the best panels, you need to keep them clean and cool.
CSP systems use mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight on a receiver. This heats up a fluid and makes steam for power. There are trough, dish engine, power tower, and linear Fresnel systems. Trough and power tower systems can reach up to 35% efficiency. Dish engine systems can reach 31.25%. CSP works best in deserts with lots of sunlight.
Hybrid solar solutions use both PV and CSP together. This helps make the system more efficient and saves money. These systems can make power even when there is not much sunlight. Hybrid systems give steady energy for big solar needs.
You should compare PV, CSP, and hybrid systems for your site. PV panels have 15% to 22% efficiency and a 20% to 30% capacity factor. CSP systems can reach 30% to 40% efficiency and have a capacity factor over 40%. Hybrid systems mix both types and give steady energy and better panel performance. New solar systems use smart designs and high-efficiency panels to make more power.

You can pick grid-tied or off-grid solar systems. Grid-tied systems connect to the main power grid. Off-grid systems work alone and use batteries for energy. The table below shows how these two types are different:
| Feature | Grid-Tied Systems | Off-Grid Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Lower, no battery storage | Higher, needs batteries and extra equipment |
| Reliability | Backup power from the grid | Full energy independence, but risk of shortages |
| Maintenance | Fewer parts, less upkeep | More battery care and replacements |
| Energy Independence | Depends on the grid | Fully self-reliant |
| Power Outages | Stops during grid outages | May run out during low sunlight |
Grid-tied solar systems cost less and are easy to take care of. Off-grid solar systems give you more control but need more planning.
You can build your solar system as centralized or distributed. Centralized systems use one big solar plant. Distributed systems use many small solar units around your site. Here is a quick look at both:
| System Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized | Easy to scale, steady performance | High costs, land needs, grid losses |
| Distributed | More control, less grid loss, efficient | Harder to manage, weather can affect output |
Centralized solar systems are good for big sites with high energy needs. Distributed solar systems are better for sites with less space or where you want more control.
You also need to pick fixed or tracking mounts for your solar panels. Fixed mounts stay in one spot. Tracking mounts move and follow the sun. This choice changes how much energy you get and how much care you need:
| Mount Type | Energy Yield Increase | Maintenance Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed-Tilt | Baseline | Low, just cleaning and checks |
| Single-Axis Tracker | 12-25% more | Higher, moving parts need attention |
Tracking mounts make more solar energy but need more care.
You should match your solar system to your industry. Food plants need steady cooling, so a centralized solar system with grid-tied backup is good. Aluminum plants can use distributed solar systems for flexible energy use. Cement and steel plants need strong solar systems because they use a lot of energy. Always check your site’s space, energy needs, and weather before you pick a solar system.
Tip: You can get more solar energy by using tracking mounts and a distributed system if your site has space and changing sunlight.

When you look at industrial solar power, you need to check many things. These things help you see how well your system works. They also show how much energy you make and how much money you save. You can use these numbers to choose the best system for your site.
Efficiency shows how much sunlight your panels turn into electricity. Power output tells you how much energy your system can make. You measure these under Standard Test Conditions. These use 1000 W/m² of sunlight, a cell temperature of 25°C, and an air mass of 1.5. These numbers help you compare different solar panels.
Efficiency tells you how much energy you get from the sun.
Power output shows the highest amount your panels can make.
If your panels are more efficient, you need less space for the same energy.
Tip: Always check efficiency and power output before you buy solar panels. This helps you plan your energy use and costs.
Degradation rate tells you how fast your panels lose power each year. Most panels lose between 0.5% and 1% of their power every year. High-quality panels lose only 0.25%. After 20 years, your panels should still make about 90% of their first output.
| Degradation Rate | Description |
|---|---|
| 0.5% - 1% | Typical annual degradation for industrial solar panels. |
| 0.25% | Degradation for high-quality panels. |
| 0.5% - 0.75% | Standard degradation range for most panels. |
| 0.75% | Median performance loss for the U.S. PV fleet. |
Degradation makes your panels less efficient and lowers energy.
Lower degradation means you get more energy and save more money.
You should plan to replace or upgrade panels as part of your system care.
Energy generation density shows how much energy you make in a certain area. Utility-scale solar systems have higher density than home systems. You want high energy density for industrial solar power. This means you get more energy from less space.
| Installation Type | Mean Power Density | Energy Density |
|---|---|---|
| Residential PV | Data from regions | Data from regions |
| Utility-scale PV | Higher density | Higher density |
High energy density helps you use your space better.
You can get more density by using better panels and tracking mounts.
How much energy you get depends on sunlight and your system setup.
Availability shows how often your system works like it should. Performance ratio (PR) tells you how much sunlight your system turns into energy you can use. You want high numbers for both.
| Metric | Standard Value |
|---|---|
| Performance Ratio (PR) | Above 80% |
| Availability | 98% or more |
High availability means your system works almost all the time.
A high performance ratio means you get more energy from your panels.
You can make these numbers better with regular care and good design.
Cost per kWh tells you how much you pay for each unit of energy. Maintenance keeps your system working well and saves you money. You want low costs and easy care for your solar system.
Lower cost per kWh means you save more money.
Cleaning and checking your system keeps it working well.
You should plan to replace batteries and upgrade inverters.
Note: Good care makes your system work more and make more energy. This gives you better results in real life.
Mass production efficiency looks at how well you make and use many solar panels. You need to keep panels clean, use tracking systems, and design your system well. Where you put your system and how you face it matters a lot. Shade can lower your energy.
Clean panels work better and last longer.
Tracking systems help you get more energy by following the sun.
Good design and site choice make your system work better.
You use these numbers to make smart choices for your solar system. These numbers help you pick the right panels, plan your site, and save money. They also help you get more energy and better results.
| Performance Metric | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Efficiency | Lowers customer costs and helps get more people to use solar. |
| Project Cycle Time | Makes projects finish faster and keeps customers happy. |
| System Uptime & Output Reliability | Makes more money by making power all the time and lowers costs with good care. |
| Incentive Utilization & Regulatory Compliance | Helps you get more money from programs and follow rules. |
You get more value from your system when you use these numbers.
High performance means more energy and lower costs.
You can make your business better and reach your energy goals.
Tip: Always check your system’s numbers. This helps you find problems early and keep your system working well.
You can use these numbers to compare different systems and pick the best one for your needs. You get more energy, higher capacity, and more savings when you use these numbers in your planning and work.
You can look at different solar technologies by seeing how they work and what they do best. The table below shows how PV, CSP, and hybrid systems do in important areas:
| Metric | PV Systems | CSP Systems | Hybrid Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High with cooling | Stable with grid support | Combines both |
| Capacity Utilization Factor | Changes with design and weather | Linked to grid stability | Uses both for better results |
| Key Performance Indicators | Sunlight, losses, temperature | Grid stability | Mix of both |
Hybrid systems use the good parts of PV and CSP. They help make the system work better and more often.
You should think about how each setup changes cost and the environment. The table below compares four common setups:
| Configuration | Cash Flow Trajectory | CO2 Emissions (tons) | GWP Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Config. 1 | Most cost-effective | 531.7 | Lowest |
| Config. 2 | Moderate | 585.5 | Higher |
| Config. 3 | Higher | 590.0 | Higher |
| Config. 4 | Higher | 590.0 | Higher |
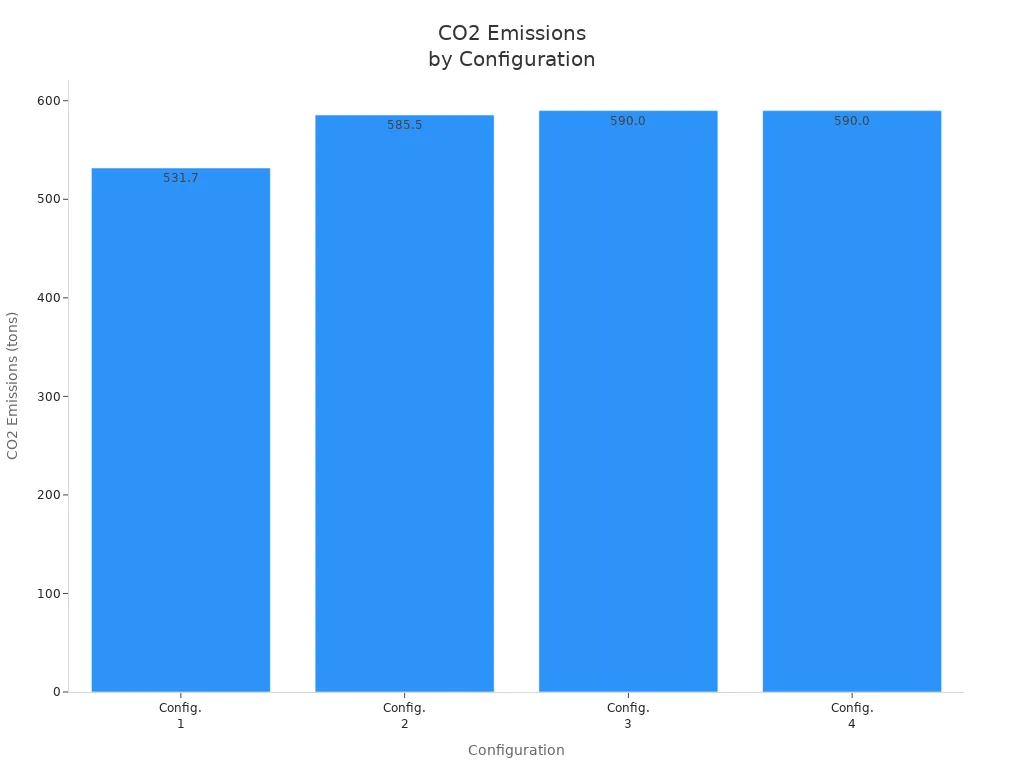
Config. 1 is best for the environment. It makes less CO2 and saves the most money. Using less energy when making and finishing the system helps lower the impact.
When you compare solar power choices, you should check these important numbers:
Net Present Value (NPV) shows how much your system is worth over time.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) tells you how much money you get back.
Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS) shows how much it costs to store energy.
Capacity Credit tells you how much steady power you get at busy times.
You should also know that things like grid changes and how much sun you get can change what is best for your site. Each system changes cost, how well it works, and how it affects the environment. You can use these tables and numbers to pick the best solar system for you.
You need to pick a solar system that fits your business. First, find out how much energy your company uses. Look at where your solar panels will go and which way they face. This helps you get the most sunlight. Think about how much money you can spend now and how much you might save later. You also need to know the rules in your state before you start.
You can use special tools to help you choose. These tools help you compare your choices and find the best one for your business:
| Decision-Making Framework | Description |
|---|---|
| AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process) | Lets you set what is most important to you. |
| TOPSIS | Shows which choice is closest to the best one. |
| Choosing by Advantages (CBA) | Looks at the good things about each choice. |
Tip: Try these tools to help you pick the best solar system for your company.
Where you put your solar system changes how well it works. You need to check if the land is dirty or has hills. You should also see if you are close to power lines. Bad weather, like floods or storms, can hurt your system.
| Factor | Impact on Feasibility |
|---|---|
| Site Contamination | You might need to clean the land first. |
| Topography | Hills change where panels go and how much energy you get. |
| Climate Risks | Floods and storms can break your system. |
| Access to Infrastructure | You need to connect your system to the power grid. |
You should also look at how much sun and heat your site gets. These things change how much energy your system makes. A good solar study checks the weather and sunlight to see how your system will work over time.
You need to think about efficiency, cost, and how well your system works. Panels that work better give you more energy but cost more. Mono-crystalline silicon panels work well and last a long time. Poly-crystalline silicon panels cost less but may not work as well.
| Efficiency Type | Cost Implication |
|---|---|
| High-efficiency modules | Cost more at the start |
| Mono-crystalline silicon | Good at making energy and last long |
| Poly-crystalline silicon | Cheaper but not as efficient |
You should also think about how fast your panels lose power. Some panels lose power faster because of certain problems. Good panels and strong warranties help protect your money. Always check what your warranty covers and think about getting insurance for extra safety.
Note: The best solar system for your business gives you the energy you need, works well at your site, and balances cost, efficiency, and reliability.
You can compare industrial solar power systems by checking important numbers. These numbers include capacity factor, performance ratio, specific yield, and system uptime. The table below shows what each number means:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Capacity Factor | Shows actual energy output compared to maximum possible output. |
| Performance Ratio | Measures how much energy you get after losses. |
| Specific Yield | Tells you energy output per installed capacity. |
| System Uptime | Tracks how often your system works as planned. |
When you use these numbers, you can make better choices. You can save money and use more of your own energy. This also helps the environment. You should pick a system that matches your site and what your business needs.
Pick solar technologies and setups that work for you.
Think about how well panels work, what inverter you use, and if you need batteries.
Make a plan to save money for a long time and keep your system working well.
You get clean energy and pay less for electricity. Solar power helps you care for the planet. It lowers your carbon footprint and helps nature. Solar systems are good for big buildings like factories and warehouses.
You check how efficient the panels are and how much power they make. You also look at how fast they lose power each year. You check how much energy is made in a certain area and how often the system works. These numbers help you compare different systems. Sustainability metrics show if your system helps you reach long-term energy goals.
Solar panels still make energy when it is cloudy. You get less power, but the system keeps working. Batteries help you save energy for cloudy days. Grid-tied systems give you backup power if you need it.
You pay for panels, inverters, batteries, and putting the system in. Where your site is, how big your system is, and how much care it needs also change the cost. You save more money over time if you plan well and take care of your system. Being sustainable helps you save money in the future.
You look at how much energy you need and what your site is like. You check your budget and compare different technologies and setups. You look at how well the system works and if it is sustainable. You use special tools to help you pick the best system for your company.
Revolutionizing Energy Use in Industrial Parks | The Qingyuan Yili 4.33MWp PV Project
Industrial PV System | 11.47MWp Rooftop Distributed Solar Power Project
Business model of industrial as well as commercial power storage space
Commercial Solar Power Systems: Benefits, Costs, and Implementation
PERC Solar Panel Efficiency: Why They're Ideal for Bifacial Module Construction
PERC Solar Cell Technology: The Foundation of Modern Bifacial Solar Modules