Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-05 Origin: Site
Bifacial solar panels are a big step for clean energy. Unlike regular panels, they collect sunlight from both sides. This design helps them make up to 30% more energy. They are a smart way to use solar power efficiently.
New technology has helped bifacial panels become more popular worldwide. By 2023, their market value was $4.5 billion. Experts think it will grow to $19.3 billion by 2032. These panels make 5.5% more energy than regular ones. They also help the environment by using more solar power and supporting green energy goals.
Bifacial panels are liked for being strong and flexible. They work well in many places, like farms or open fields. Their see-through design saves space and fits into modern buildings. This makes them a top choice for solar energy projects everywhere.

Bifacial solar panels take in sunlight from both sides. This boosts energy production by up to 30%.
These panels work well on reflective surfaces like snow or sand. This makes them more efficient in different places.
Installing them correctly is very important. Height, tilt, and spacing can improve energy output a lot.
Bifacial panels are strong and often have no frame. They resist weather damage and come with long warranties.
They can be used in many ways, like on farms or in factories. This helps save space and make more energy.
They cost more at first but save money over time. They also give better returns on investment.
These panels work well even in low light. They are useful on cloudy days too.
More people are buying bifacial panels as technology improves. The demand for clean energy is also growing fast.
Bifacial solar panels use two kinds of sunlight: direct sunlight and reflected light. Direct sunlight hits the front of the panel. Reflected light bounces off surfaces like the ground or buildings and reaches the back. This two-sided design helps make more energy, especially in shiny places like snowy fields or near water.
Research shows bifacial panels can make up to 30% more power than regular panels. They collect sunlight from both sides, which increases energy production. This makes them great for areas with scattered light or reflective surfaces.
The photovoltaic effect is how sunlight turns into electricity. When sunlight hits the solar cells, it moves electrons, creating an electric current. Bifacial panels improve this by using sunlight on the front and reflected light on the back. This two-sided energy collection boosts power, especially in reflective areas.
For example, panels on building walls or roofs can make 11% more energy, according to Chen et al. (2021). Ledesma et al. (2020) found a 7-8% energy increase from sunlight hitting the back.
The bifaciality ratio shows how well the back works compared to the front. It is calculated as:
This ratio is usually between 0.6 and 0.9, meaning the front side works better.
Other performance measures include the bifaciality coefficient, which compares energy points (like Isc, Voc, and Pm) under perfect conditions. Outdoor tests measure the highest power bifaciality coefficient. These results are adjusted to standard test conditions (STC) using simple math.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Bifaciality Coefficient | Compares rear and front energy points in perfect conditions |
| Real Operating Conditions | Outdoor tests measure maximum power bifaciality coefficient |
| Measurement Translation | Results adjusted to STC using simple calculations |
| Irradiance Impact | Lower sunlight reduces bifaciality coefficient in a straight line |
| Non-linear Increase | Bifaciality rises quickly at sunlight below 200 W/m² |
Bifacial panels are made to create more energy. Common features include:
Bifaciality ratios between 0.6 and 0.9.
Better performance in shiny places like snowy fields or water.
Can be used on the ground or in buildings.
Ground reflectivity, or albedo, helps bifacial panels make more energy. Shiny surfaces like snow, sand, or white paint bounce more sunlight to the back of the panels. Tests show that reflectors can raise yearly energy output by up to 4.5%.
| Reflector Coverage | Annual Energy Yield Increase |
|---|---|
| 100% | Up to 4.5% |
| 50% (centered on torque tube) | Up to 4.5% |
| 25% (centered on torque tube) | Up to 4.5% |
To get the most energy, bifacial panels need to be installed correctly:
Height: Raising panels lets more reflected light reach the back.
Tilt Angle: Tilting panels helps catch sunlight on both sides.
Spacing: Leaving space between rows reduces shadows and improves light on the back.
Things like ground reflectivity, panel height, and row spacing affect energy output. Users can adjust these settings for the best results at their location.

Bifacial solar panels make more electricity than regular ones. They collect sunlight from both sides, boosting energy by up to 30%. Studies by Sun et al. (2018) and Kopecek and Libal (2021) show these panels work best on shiny surfaces like snow or sand.
Key Findings:
Energy increases by 10% to 30% on reflective surfaces.
Two-sided light capture works well in areas with scattered light.
For example, the VBPV system at the University of York shows how bifacial panels work in real life. With a 3-kW inverter, it collects more sunlight and tracks energy production. This proves bifacial panels can produce more power in everyday use.
Bifacial panels are great in dim or scattered sunlight. Unlike regular panels, they use reflected and diffused light to keep making power. This makes them useful in cloudy places or during mornings and evenings when sunlight is weaker.
Tip: If your area has cloudy weather, bifacial panels can give you better energy results than regular ones.
Bifacial panels are built to last. Their frameless design and tempered glass protect them from weather. They resist moisture, UV rays, and stress, making them last longer.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Wind and Storm Resistance | Handles strong winds and hail without breaking. |
| Temperature Tolerance | Works well in very hot or freezing weather. |
| Moisture and Humidity Protection | Stops water from damaging the inside parts. |
| Warranty | Usually comes with a 25 to 30-year warranty, keeping at least 80% efficiency over time. |
This strong design lowers the chance of damage and reduces repair costs. The glass-glass build also makes them tougher, perfect for long-term solar projects.
Bifacial panels often have longer warranties because they are so durable. Most come with 25 to 30 years of guaranteed performance. Even after many years, they keep at least 80% of their original efficiency.
Note: Longer-lasting panels mean better savings and returns over time.
Bifacial panels can be used in many ways. They work for homes, businesses, and even off-grid setups.
Examples of Use Cases:
Residential: Homeowners like John Doe in California saw 30% more power with bifacial panels.
Commercial: Companies like 'Tech Giants Inc.' use bifacial panels in parking lots to save energy and look eco-friendly.
Bifacial panels use space better by making more energy per square foot. Their see-through design fits well with modern buildings, like solar roofs or walls. This makes them a great choice for cities where space is tight.
| Benefit Type | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Land Use | Produces more energy in less space. |
| Aesthetic Integration | Works as clear solar roofs or walls in stylish buildings. |
With their mix of function and style, bifacial panels are a smart choice for clean energy in both rural and city areas.

Bifacial solar panels cost more than regular ones. This is because they need special materials and extra steps to make. Both sides have tempered glass, and the solar cells are advanced, which raises the price.
Reasons for higher costs:
Bifacial panels cost more per watt than regular panels.
Extra costs for mounts and inverters also add up.
Even though they make more energy, the high price can be a problem. Big projects might save money over time, but small ones may find the cost too high.
Setting up bifacial panels is trickier than regular ones. They need to be placed carefully to catch sunlight on both sides. This often means hiring experts, which costs more.
Installation challenges include:
Raised mounts are needed to use the back side.
Extra time and effort are required for proper setup.
These issues make installation more expensive and harder for small or DIY projects.
Bifacial panels weigh more because of their double-glass design. This can be too much for older or weaker roofs. They also need to be raised to work well, which is hard for most homes.
| Problem | Why It Happens |
|---|---|
| Heavy Panels | Double-glass design adds weight, stressing rooftops. |
| No Backside Energy Gain | Flat roof setups block reflected light, lowering energy output. |
If your roof can't handle the weight or raising the panels, these might not work for you.
Bifacial panels need open spaces and reflective surfaces to work best. Most home roofs don’t have these conditions. If placed flat on a roof, the back side won’t get sunlight, losing one of their main benefits.
Other problems include:
Heat builds up because of the glass, making them less efficient.
They can break more easily during installation due to the glass.
These issues make bifacial panels less useful for homes. They are better for big projects, but their downsides for houses are hard to ignore.
Bifacial solar panels cost more because they use special materials. They have tempered glass on both sides to protect the cells. This design makes them stronger but harder to produce. The solar cells are made to catch sunlight from both sides, which adds to the cost.
Special mounts are needed to lift the panels for better sunlight capture. These mounts make installation harder and take more time. While the upfront cost is higher, the panels last longer and work better. This makes them a smart choice for big solar projects.
Bifacial panels are pricier than regular ones. They cost about 10-20% more per watt because of their design. For example, a regular panel might cost $0.30 per watt, while a bifacial panel costs $0.35 to $0.40 per watt.
The extra cost pays off with more energy production. Bifacial panels can make up to 30% more power, especially in shiny places like snowy fields. Over time, this extra energy lowers the overall cost, making them a good long-term choice.
Bifacial panels cost more upfront but make more electricity. They catch sunlight from both sides, producing extra power in reflective areas. Using solar trackers with bifacial panels can cut costs by 16% compared to regular systems.
Many people are choosing bifacial panels because they save money over time. In 2023, solar energy made up 75% of new renewable energy worldwide. This shows how popular bifacial panels are becoming. Their extra energy helps balance the initial cost, giving a good return on investment.
The bifacial solar panel market is growing fast. By 2025, it could be worth $15 billion and reach $60 billion by 2033. This growth is driven by better technology and lower production costs.
Between 2023 and 2028, the market is expected to grow even faster. Over 250 million panels might be sold by 2028. As production becomes cheaper, bifacial panels will cost less and be easier to buy. This means more people can use them, combining great performance with lower prices in the future.

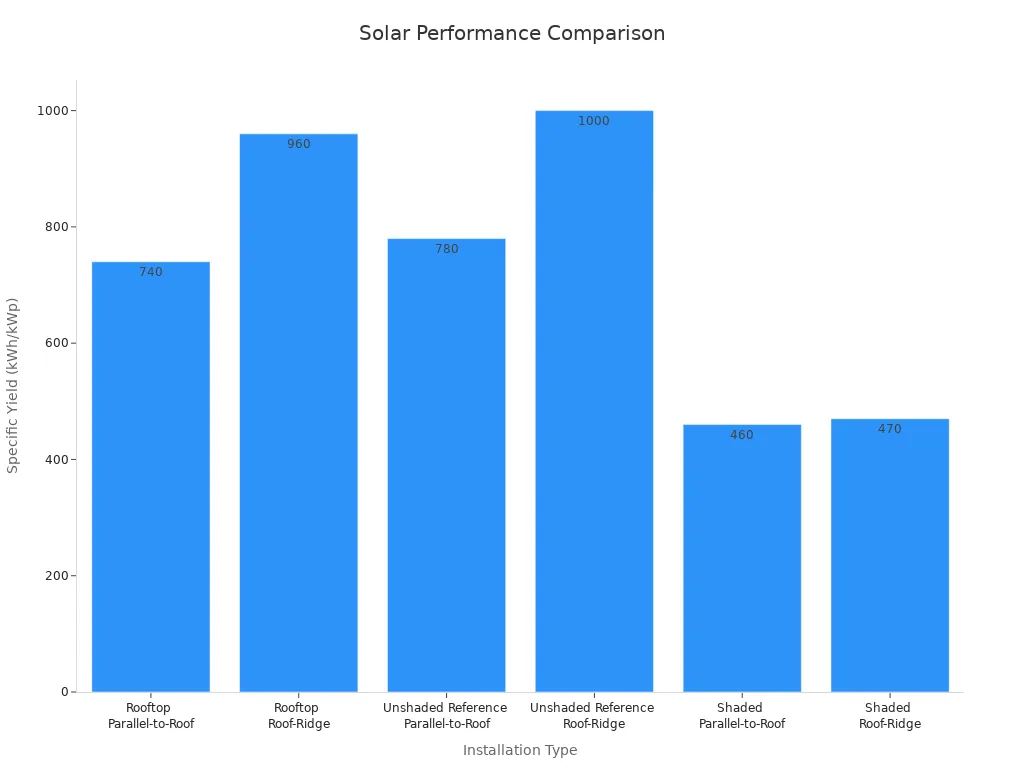
Bifacial solar panels work well for big commercial projects. They collect sunlight from both sides, making them great for ground-mounted systems and rooftops. Ground setups benefit from shiny surfaces like snow or sand, which reflect light and boost energy. Rooftop systems, especially those placed along roof ridges, also perform efficiently. These systems can produce between 740 to 960 kWh/kWp each year.
One study showed a 6.8 kWp bifacial system produced 1569 kWh/kWp annually. This proves how effective bifacial panels are for large-scale energy needs. Most bifacial panels are used in commercial projects, showing they meet high-energy demands well.
Pairing bifacial panels with batteries makes them even better. Batteries store extra energy made during sunny times. This stored power can be used when sunlight is low. Businesses save money by using less grid power. Bifacial panels make more energy, so they fill batteries faster. This setup is a smart choice for industrial solar systems.
Agrivoltaics mixes farming with solar energy. Farmers use bifacial panels to make power while growing crops. The panels provide shade, keeping soil cooler and saving water. This setup improves planting conditions and boosts land use. It’s a great solution for rural areas.
Panels help crops grow better by controlling temperature and humidity.
Farmers can grow valuable crops under panels, earning more money.
Solar energy offsets any crop losses, keeping farms profitable.
Bifacial panels create better conditions for crops. They reduce soil heat and water loss, leading to healthier plants. Farmers save on irrigation and earn by selling extra solar power.
| Aspect | Findings |
|---|---|
| Economic Impact | Farmers earned more by balancing crop losses with solar energy profits. |
| Crop Yield | Panels improved crop growth and lowered farming costs. |
| Water Conservation | Shading reduced water use by lowering soil evaporation. |
Bifacial panels are useful for off-grid setups. They work well in carports and parking lots, where light reflects off paved surfaces. Portable bifacial systems are great for remote areas, offering reliable power. Their strong design and high energy output make them ideal for special uses.
Fixed tilt systems make up to 11% more energy.
Tracker systems increase energy by up to 27%.
Smaller setups cost less and save space for off-grid needs.
In cities, bifacial panels fit into building designs as BIPV systems. They can be used as windows, walls, or roofs, combining style with function. These panels save space and support green city projects.
Bifacial panels, with power ratings of 250 to 400 watts, work well in BIPV setups. They last long and resist UV damage, making them a solid choice for urban solar systems.
Bifacial panels have a clear back or double glass layers. This lets them collect sunlight from both sides. Monofacial panels only absorb sunlight from the front because of their solid back. Bifacial panels work better in shiny places like snowy fields or sandy areas. Their design uses reflected light to make more energy.
| Factor | Bifacial Panels | Traditional Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Albedo | Needs shiny surfaces for best results | Works fine without shiny surfaces |
| Panel Height | Raised about 1 meter for better energy | Normal height |
| Tilt | Tilted 2-15 degrees more than monofacial panels | Fixed tilt |
| Row Distance | 6-8 meters apart for best performance | Standard spacing |
| Energy Yield | Makes 20-39% more energy in good conditions | Lower energy output |
| Cost | Costs 15% more with tracking systems | Cheaper upfront |
Bifacial panels need special mounts and angles to work well. Monofacial panels are easier to set up because they don’t need these adjustments.
Bifacial panels make more energy in shiny places. They collect sunlight from both sides, which boosts energy production. Studies show they can make up to 25% more energy over white tiles or aluminum. Monofacial panels don’t have this feature, so they are less effective in these areas.
| Study | Technology | Performance Metric | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alam et al. | Bifacial | BG with white tiles | 14.3% - 25% |
| Ganesan et al. | Bifacial | Average BG | 4.8% (grass) - 21.4% (aluminum) |
| Ferruzzi | Bifacial vs Monofacial | Daily Energy Production | 15.24 - 16.90 kWh/day (bifacial) vs 13 - 15 kWh/day (monofacial) |
Bifacial panels make more energy than monofacial panels. They collect sunlight from both sides, giving them an average efficiency of 19.64%. Monofacial panels only reach 13.05%. In bright sunlight, bifacial panels produce 401.7 W, while monofacial panels make 391 W. In dim light, bifacial panels still perform better, making 127.4 W compared to 85.43 W.
Even though bifacial panels cost more upfront, they save money over time. They have a lower energy cost of $0.0473/kWh compared to $0.0492/kWh for monofacial panels. Their total value is also higher, reaching $44,167.06 versus $38,359.67 for monofacial panels.
| Metric | Bifacial ($) | Monofacial ($) |
|---|---|---|
| LCOE ($/kWh) | 0.0473 | 0.0492 |
| NPV ($) | 44,167.06 | 38,359.67 |
| DPBP (years) | 13.93 | 14.97 |
| IRR (%) | 8.661 | 8.074 |
| PI | 1.372 | 1.309 |
Bifacial panels work well in places with shiny surfaces or scattered light. They are great for farms, factories, and city buildings. Monofacial panels are cheaper and better for homes or small spaces.
Tip: Use bifacial panels for open areas or shiny surfaces to get more energy and save money over time.
Bifacial solar panels are a big step in clean energy. They collect sunlight from both sides, with a bifaciality rate of 70%. The front side makes 500 watts, and the back adds 350 watts. This two-sided design helps them make more energy, making them great for large solar projects.
These panels are strong and produce more power, but they cost more and are harder to install. Still, their long-term benefits make them worth it, especially for businesses. Experts predict the market will grow to $72.32 billion by 2034. This growth is helped by new technology and government support, like the Inflation Reduction Act.
Why They’re Growing:
More energy for less money per kilowatt-hour.
Bigger investments in green energy and government help.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Bifaciality Rate | 70% |
| Front Power Generation | 500 watts |
| Back Power Generation | 350 watts |
More people are using bifacial panels to help the planet. They work well for big solar farms and city buildings, offering a smart way to use clean energy.
Bifacial panels take in sunlight from both sides. Monofacial panels only use the front side. This two-sided design helps make more energy, especially in places with shiny surfaces like snow or sand.
Yes, they are great for big projects. While they cost more upfront, they can make up to 30% more energy. Over time, this extra energy saves money and gives better returns.
Bifacial panels are not the best for home roofs. They need to be raised and work better with reflective surfaces. Their heavy weight and tricky setup make them hard to use on most houses.
Bifacial panels work well on cloudy days. They use scattered and reflected light to keep making energy. This makes them a good choice for places with lots of clouds.
Bifacial panels last about 25 to 30 years. Their strong glass design protects them from bad weather. Most come with warranties that promise at least 80% efficiency during their lifetime.
No, they are easy to maintain. Cleaning off dirt and dust helps them work well. Their tough glass design means they are less likely to get damaged, so they need less care than regular panels.
Bifacial panels work best in open areas with shiny surfaces. Good spots include snowy fields, sandy places, or areas with white-painted ground. They also do well in business and factory setups with raised mounts.
Yes, solar trackers make bifacial panels even better. Trackers move the panels to follow the sun, helping both sides collect more light. This setup boosts energy production a lot.