Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-07-19 Origin: Site
Solar panel encapsulation makes a shield around solar cells. This shield protects them from things like water, sunlight, and heat changes. Encapsulation helps panels last longer and work well. Tests show that encapsulation lets panels keep working well for years. Some panels still have almost 19.2% efficiency after a long time. The main materials—like EVA, POE, and TPU—each have special uses for different places and needs. Studies show that good encapsulation lowers the chance of panels breaking. It also makes panels more reliable. Picking the right encapsulant helps panels last longer and work better. Encapsulants are very important for keeping solar panels safe and strong. They also help panels make power for a long time.

Solar panel encapsulation keeps solar cells safe from water, dust, heat, and sunlight. This helps panels last longer and work better.
Good encapsulation materials like EVA, POE, and silicone let sunlight in. They also protect panels from getting damaged and losing power.
Encapsulation helps panels work better by letting more light reach the cells. It also stops electrical problems inside the panel.
Picking the right encapsulation depends on your local weather and panel type. This helps make sure the panels stay strong and last a long time.
Always look for quality certifications and test results. This helps you choose solar panels with safe and reliable encapsulation.
Solar cell encapsulation means putting a cover around solar cells to keep them safe. Special materials are used to protect the cells from things like water, sunlight, dirt, and quick temperature changes. First, workers clean and line up the cells. Then, they put on the encapsulant and cover sheets. Next, they press and heat the layers to stick them together. After that, they check for bubbles or weak spots. The main goal is to make a barrier that keeps the cells safe and working well. Some important things to check are how much light gets through, how strong the layers stick, and how well the cover handles heat and sunlight. These things help the solar panel last longer and work better. If there is no encapsulation, panels stop working well very fast. Studies show that panels without good encapsulation can drop to only 13% performance. They also break and crack more, which makes them wear out faster.
The main reason for solar cell encapsulation is to keep the cells safe and working for many years. Encapsulation stops water, dust, and strong sunlight from hurting the cells. It also keeps the electricity inside the cells safe. The process makes the panels stronger, so they can handle things like hail or strong winds. Materials like EVA and silicone let in lots of sunlight, so the panels can make more power. Encapsulation helps control heat, which is important because solar cells lose about 5% power for every 10°C rise in temperature. The process also helps the panels resist fire, salt, and ammonia. Some types, like double-glass encapsulation, help the layers move together, so the cells do not get stressed. Tests show that good encapsulation lets panels survive hail at almost 100 km/h and keep working in tough weather. Encapsulation also stops lead and other bad stuff from leaking out, so the panels are safer for the environment. All these things show why encapsulation is so important for making solar panels last a long time and work well.

Solar cell encapsulation makes a strong shield for panels. This shield keeps out water, dust, and UV rays. When the weather is very hot or cold, encapsulation helps protect the panels. Scientists tested polymer encapsulants in deserts. The tests show that the right encapsulant stops UV damage and slows down aging.
Tests show that the type of encapsulation changes how fast panels wear out in the sun.
Other tests copy hot days and cold nights. Encapsulation helps stop cracks and keeps parts connected.
Tests in places like Saudi Arabia show that good encapsulation and special coatings can cut power loss from dust by up to 35%.
Encapsulation also keeps water out of the panel. This matters because water can make layers peel or cells rust. In deserts, panels get more UV and dust than in cooler places. Encapsulation helps panels work well even in these hard places.
Note: Without encapsulation, panels can lose most of their power in less than 100 hours of strong sunlight. Encapsulation keeps cells safe and helps them last for years.
Encapsulation also stops bad chemicals from leaking out. This makes solar panels safer for nature. Using the right encapsulant means fewer repairs and less chance of panels breaking early.
Encapsulation does more than just protect. It also helps panels work better and last longer. Encapsulation materials let in lots of sunlight. This helps cells make more electricity. Some new encapsulants help panels take in even more light, so they work better.
| Metric | Before Optimization | After Optimization | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency (%) | 16.5 | 21.1 | +4.6 |
| Short-circuit current density (mA/cm²) | 34.3 | 38.2 | +3.9 |
| Open-circuit voltage (mV) | 632 | 684 | +52 |
| Fill factor (%) | 76.2 | 80.8 | +4.6 |
The table shows that better encapsulation and design can make panels 4.6% more efficient. Encapsulation also gives electrical insulation. This keeps electricity safe inside the panel and stops short circuits.
Encapsulation helps panels keep working well over time. For example, strong encapsulation lets panels keep up to 98% of their starting power after 1,000 hours of heat and wetness. Panels without encapsulation lose power faster and may stop working. Encapsulation also stops lead and other bad stuff from leaking if the panel breaks.
Encapsulation also makes panels last longer. New methods, like thin film encapsulation, use new materials to help panels last. Companies like DuPont and Hoya make strong encapsulants that block water and heat. These changes help panels work well for many years, even in tough places.
Encapsulation helps panels last longer and work better. It keeps the solar panel module working its best. Encapsulation is important because it protects panels and helps them work better. This makes encapsulation a key part of every solar panel.

Image Source: pexels
Solar cell encapsulation uses different materials to keep modules safe and working well. The most common ones are EVA, POE, PVB, and silicone. Each one has special features that make it good for certain solar panels.
EVA is short for ethylene vinyl acetate. It is the most used adhesive film in solar panels. EVA sticks well and lets lots of light pass through. It is about 450 micrometers thick. It uses chemicals called peroxides to link its parts together. But, EVA can make acetic acid as it gets older. This acid can cause the module to rust. EVA also lets more water vapor pass through and has lower volume resistivity than some other materials. Many panels use high-transmittance EVA film to let in more sunlight and make more power.
| Encapsulant | Thickness (µm) | Chemical Crosslinking | Acetic Acid Formation |
|---|---|---|---|
| EVA | ~450 | Yes, with peroxides | Yes |
POE stands for polyolefin elastomer. It is another popular adhesive film for panels. POE is about 550 micrometers thick. It also uses chemical crosslinking. POE does not make acetic acid, so it helps stop rust and other problems. POE has better volume resistivity and keeps out water vapor better than EVA. This makes it good for double-glass panels and places with lots of moisture. Many companies use high-transparency POE film because it is stable in sunlight and gives good electrical insulation.
| Encapsulant | Thickness (µm) | Chemical Crosslinking | Acetic Acid Formation |
|---|---|---|---|
| POE | ~550 | Yes, with peroxides | No |
PVB means polyvinyl butyral. It is often used in building-integrated photovoltaic modules. PVB sticks well and lets in light. It blocks UV rays and keeps the layers together. PVB works well in thin-film and glass-glass panels. It does not make acetic acid, so it lasts longer.
Silicone is special because it is flexible and strong. Silicone films can stretch much more than other types. Tests show silicone can stretch over eight times more than others. It stays strong after being stretched and after sunlight, heat, and water. This makes it good for flexible panels and special designs. Other materials like TPO and ionomers give high electrical insulation and keep out water.
Note: Polyolefins and ionomers do not make acetic acid. They also have better UV stability than EVA. This makes them good for panels that need to last a long time.
The table below shows how the main films compare:
| Encapsulant | Volume Resistivity (Ω-cm) | MVTR (g/m²/day) | UV Stability | Acetic Acid Formation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVA | ~1 x 10^13 | ~1.0 | Good | Yes |
| POE | ~1 x 10^16 | ~0.22 | Excellent | No |
| Ionomer | ~2 x 10^16 | ~0.3 | Excellent | No |
Different panels need different films. Crystalline silicon panels often use EVA because it is clear. Double-glass and thin-film panels use POE or PVB for better water protection. BIPV panels may use PVB or silicone for extra strength and flexibility.
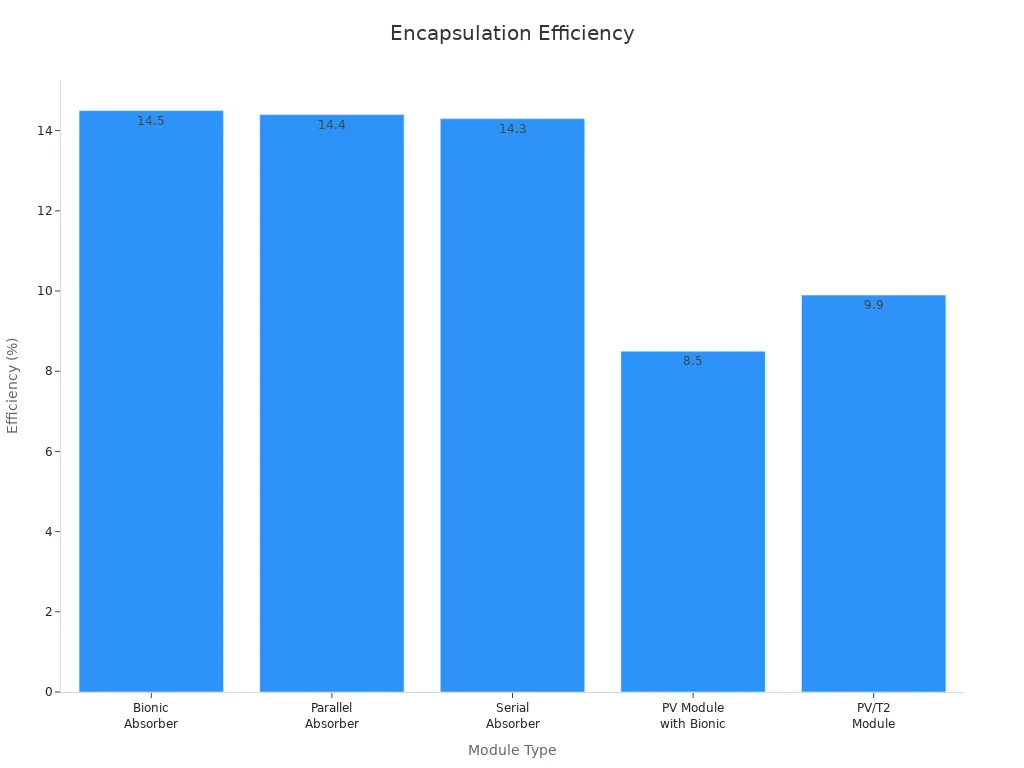
Solar cell encapsulation is very important for making panels last and work well. Picking the right film depends on the panel type, weather, and how well it needs to work.

Image Source: pexels
Solar panels can lose power over time because of PID. PID stands for Potential Induced Degradation. This happens when sodium ions move inside the panel. These ions can hurt the cells. Encapsulation helps by blocking these ions from moving. Using PET instead of soda-lime glass helps protect the cells more. The table below shows how different materials affect power loss during PID tests:
| Substrate Type | PID Stress Duration | Average Relative Efficiency Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Soda-Lime Glass (SLG) | 136 hours | 6.0% |
| Soda-Lime Glass (SLG) | 300 hours | 15% |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | 136 hours | 0.05% |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) | 300 hours | 0.11% |
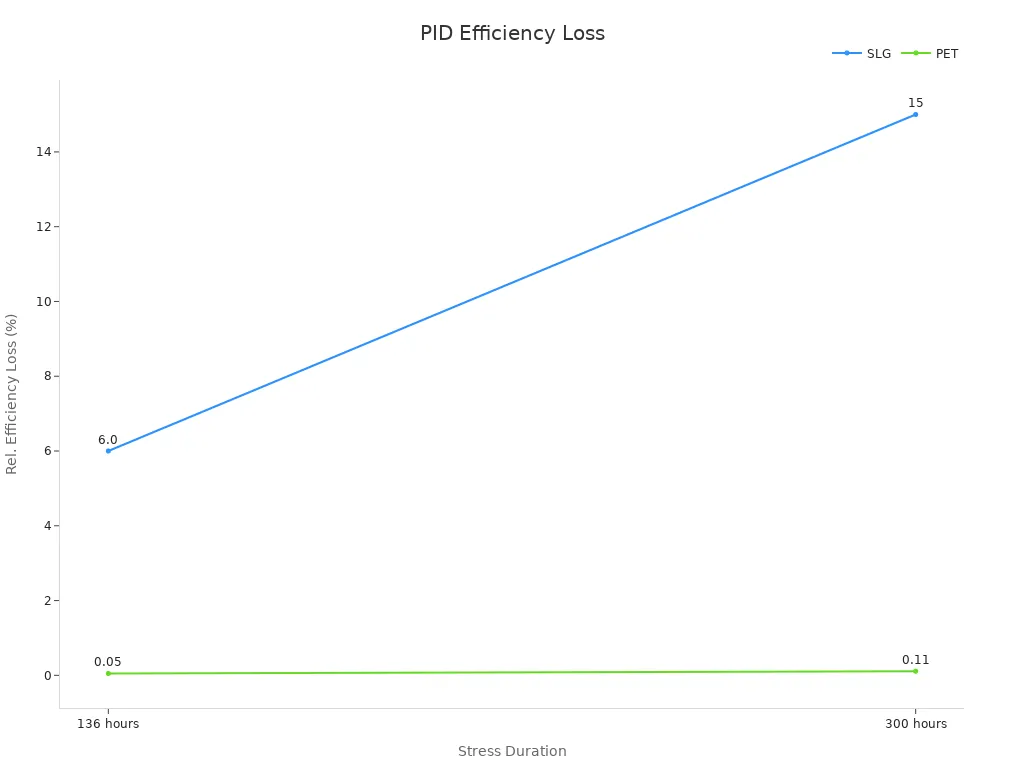
The chart shows PET stops most PID power loss. This keeps panels working better for a longer time. Good encapsulation materials act like a shield. They help stop damage and make panels last longer.
Solar panels have to deal with rain, dust, and strong sunlight. Encapsulation gives extra protection by keeping out water and dirt. This helps the inside parts stay safe and last longer. Companies test encapsulation using rules like IEC62788. These tests make sure the materials can last for many years.
Panels often have warranties for 25 years or more. These long warranties show that encapsulation works well. Special tests use UV light and heat to see how materials hold up. Results show good encapsulation keeps protecting for many years. This means panels stay strong and keep making power, even in tough places.
Tip: Always pick panels that meet strict quality rules. This gives the best protection against damage and power loss.
Picking the best encapsulation process depends on a few things. The weather in your area is very important. Hot and wet places need materials that block water and UV rays. POE and special silicones help panels last longer in these places. Cold or mountain areas need flexible materials that do not crack. EVA or thermoplastic elastomers work well in cold weather.
The kind of panel you have also matters. Crystalline silicon panels often use EVA because it is cheap and works well. Newer solar panels, like n-type TOPCon or Si-heterojunction, use POE or special mixes. These help the panels work better and last longer. Some companies, like RenewSys and JA Solar, make panels with new ways to stop cracks and water damage.
The table below shows how common materials compare:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| EVA | Good flexibility, UV stable | Cost-effective, easy to use | Can yellow, forms acetic acid |
| POE | High resistivity, UV stable | No discoloration, good for double-glass | Lower adhesion |
| Silicone | Flexible, UV transparent | Strong in harsh climates | Needs special processing |
| PVB | UV blocker, strong bond | Good for glass-glass | Absorbs water |
Tip: Some new materials have extra layers or special chemicals. These can help panels last longer and work better in hard places.
When picking an encapsulation process, check for good quality and safety. Make sure the panels meet world standards like IEC62788. They should pass long tests outside. The maker should give safety sheets and show the panels do not give off bad gases. Clean rooms and good records mean the panels are made well.
Check if the company has a good name and real stories.
Ask for test results, like Hi-Pot or continuity tests.
Pick materials that last in your local weather.
Think about how easy it is to put in and take care of the panels.
Tests in Europe and Asia show the right process keeps panels working for over 25 years. UV pictures and power checks help see how old the panels are and how long they will last. If you follow these tips, you can pick materials that keep panels safe, help them work better, and make sure they last a long time.
Encapsulation keeps water, dust, and UV rays away from solar panels. This helps the panels last longer. Picking good materials helps solar panels work better and stay strong for more years. Experts say you should always check for quality and safety standards. This makes sure the panels are safe and work well.
Some new encapsulation materials, like UV-curable resins and recyclable films, stop water from getting in better and help the environment.
More people are using advanced encapsulation. These new solutions help solar panels last even longer.
Solar panel encapsulation makes a cover for solar cells. This cover keeps out water, dust, and sunlight. It helps the panels last longer and work better. Encapsulation also keeps the electricity inside safe.
POE and silicone last the longest. They are very good at stopping water and sunlight. Many experts pick these for panels in hard weather.
Tip: POE is best for double-glass panels and rainy places.
Yes! Good encapsulation lets more sunlight get to the cells. This helps the panel make more electricity. Some new materials can make panels up to 5% better.
Look for certifications like IEC62788.
Ask the maker for test results.
Check if the company is trusted.
| Checkpoint | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Certification | Shows good quality |
| Test Results | Proves how it works |
| Reputation | Means you can trust them |
CIGS vs Flexible Monocrystalline Solar Panels Which One Should You Choose
What Are CIGS Solar Panels and How Do They Compare to Silicon Panels
How Many Solar Panels Do You Need to Run a 1.5 Ton Air Conditioner in 2025
What drives solar panel efficiency and how to get the most energy
Horizontal vs Vertical Solar Panels Installation : Which Orientation Maximizes Efficiency